
Matrix: Priebel/130bit
Description: Quadratic sieve; factoring a 130bit number. D. Priebel, Tenn. Tech Univ
 |
| (bipartite graph drawing) |
 |
 |
 |
| Matrix properties | |
| number of rows | 584 |
| number of columns | 575 |
| nonzeros | 6,120 |
| structural full rank? | no |
| structural rank | 566 |
| # of blocks from dmperm | 45 |
| # strongly connected comp. | 9 |
| explicit zero entries | 0 |
| nonzero pattern symmetry | 0% |
| numeric value symmetry | 0% |
| type | binary |
| structure | rectangular |
| Cholesky candidate? | no |
| positive definite? | no |
| author | D. Priebel |
| editor | T. Davis |
| date | 2009 |
| kind | combinatorial problem |
| 2D/3D problem? | no |
| Additional fields | size and type |
| factor_base | full 575-by-1 |
| smooth_number | full 584-by-20 |
| solution | full 261-by-1 |
Notes:
Each column in the matrix corresponds to a number in the factor base
less than some bound B. Each row corresponds to a smooth number (able
to be completely factored over the factor base). Each value in a row
binary vector corresponds to the exponent of the factor base mod 2.
For example:
factor base: 2 7 23
smooth numbers: 46, 28, 322
2^1 * 23^1 = 46
2^2 * 7^1 = 28
2^1 * 7^1 * 23^1 = 322
Matrix:
101
010
111
A solution to the matrix is considered to be a set of rows which when
combined in GF2 produce a null vector. Thus, if you multiply each of
the smooth numbers which correspond to that particular set of rows you
will get a number with only even exponents, making it a perfect
square. In the above example you can see that combining the 3 vectors
results in a null vector and, indeed, it is a perfect square: 644^2.
Problem.A: A GF(2) matrix constructed from the exponents of the
factorization of the smooth numbers over the factor base. A solution of
this matrix is a kernel (nullspace). Such a solution has a 1/2 chance of
being a factorization of N.
Problem.aux.factor_base: The factor base used. factor_base(j) corresponds
to column j of the matrix. Note that a given column may or may not have
nonzero elements in the matrix.
Problem.aux.smooth_number: The smooth numbers, smooth over the factor
base. smooth_number(i) corresponds to row i of the matrix.
Problem.aux.solution: A sample solution to the matrix. Combine, in GF(2)
the rows with these indicies to produce a solution to the matrix with the
additional property that it factors N (a matrix solution only has 1/2
probability of factoring N).
Problem specific information:
n = 787911249838484617926390474950774839909 (130-bits)
passes primality test, n is composite, continuing...
1) Initial bound: 10000, pi(10000) estimate: 1085,
largest found: 8707 (actual bound)
2) Number of quadratic residues estimate: 725, actual number found: 574
3) Modular square roots found: 1148(2x residues)
4) Constructing smooth number list [sieving] (can take a while)...
Sieving for: 584
5. Constructing a matrix of size: 584x575
Matrix solution found with: 261 combinations
Divisor: 23850290715477455017 (probably prime)
Divisor: 33035708421246870877 (probably prime)
| Ordering statistics: | result |
| nnz(V) for QR, upper bound nnz(L) for LU, with COLAMD | 56,434 |
| nnz(R) for QR, upper bound nnz(U) for LU, with COLAMD | 64,716 |
| SVD-based statistics: | |
| norm(A) | 30.5208 |
| min(svd(A)) | 7.22461e-17 |
| cond(A) | 4.22456e+17 |
| rank(A) | 566 |
| sprank(A)-rank(A) | 0 |
| null space dimension | 9 |
| full numerical rank? | no |
| singular value gap | 8.13682e+12 |
| singular values (MAT file): | click here |
| SVD method used: | s = svd (full (A)) ; |
| status: | ok |
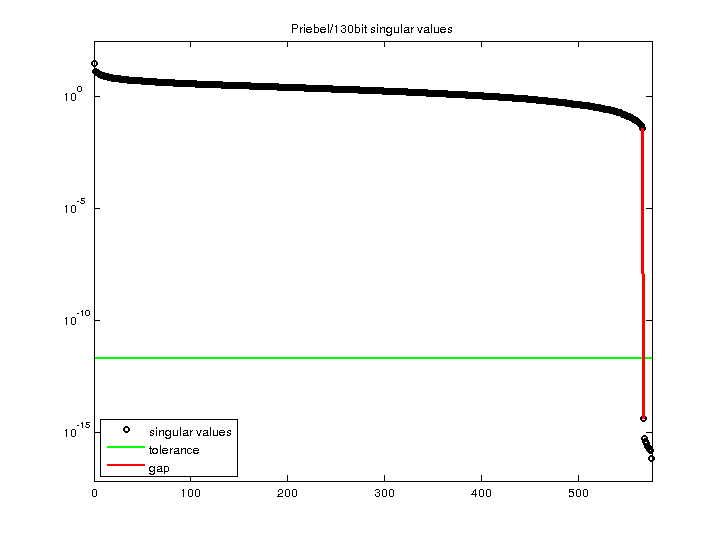
For a description of the statistics displayed above, click here.
Maintained by Tim Davis, last updated 12-Mar-2014.
Matrix pictures by cspy, a MATLAB function in the CSparse package.
Matrix graphs by Yifan Hu, AT&T Labs Visualization Group.