Cryptology - I: Appendix C - Review of Cryptosystems
In this class, we often express cryptologic operations in terms of
a formal notation. This section contains an overview of notation
associated with cryptographic transforms (Section C-1) and cryptosystems
that incorporate such trnsforms (Section C-2). In Section C-3, we
discuss information-theoretic concepts of data security, and summarize
high-level formalisms associated with cryptanalysis in Section C-4.
C-1. Cryptographic Transforms.
An encryption or decryption transform accepts a message and a
key and yields another message. In the encryption step, the
input message is plaintext and the output is ciphertext. For
decryption, the input (ciphertext) is transformed into plaintext at
the transform's output.
-
Definition. An encryption transform TE
: FX × K -> GY, where
K denotes the keyspace and G = F or
X = Y is usual. Here, the input of TE is
plaintext and the output is ciphertext.
Observation. If |Y| > |X|, then we call
the output of TE a homophonic cipher.
Definition. A decryption transform TD
: GY × K -> FX, where
K denotes the keyspace and G = F or
X = Y is usual. Here, the input of TE is
ciphertext and the output is plaintext.
Observation. Let k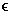 K
and plaintext
a
K
and plaintext
a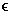 FX.
It is customary that a =
TD(TE(a)).
FX.
It is customary that a =
TD(TE(a)).
C-2. Cryptosystems.
The fundamental purpose of cryptography is to enable two parties to
communicate over an insecure channel such that an adversary cannot
understand their communication. This concept can be expressed
formally in terms of the following notation.
-
Definition. A cryptosystem is a five-tuple
(P,C,K,E,D), where
- P is a finite set of possible plaintexts;
- C is a finite set of possible ciphertexts;
- K, the keyspace, is a finite set of possible keys; and
- E and D are sets of encryption and decryption
transforms;
such that a = TD(TE(a)),
for all a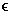 P.
P.
Observation. Let us call the two parties conversing over a secure
channel Alice and Bob, and the adversary will be named
Oscar. The paradigm for secure communication with cryptographic
protocols is illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Alice sends a message a to Bob over an insecure
channel as ciphertext c, with a key sent to Bob over a secure
channel. Meanwhile, Oscar listens to the insecure channel, which he
can intercept. The dotted line indicates that Alice controls the keysource.
-- TO BE CONTINUED --
C-3. Concepts of Security.
C-4. Cryptanalytic Oracles.
This concludes our discussion of cryptosystems for this class.
Additional statistical concepts will be defined as they are introduced in
theory development.
References
[Mau91]
Maurer, U.M. "A universal statistical test for random bit generators",
In A.J. Menezes and S. A. Vanstone, Eds., Proceedings CRYPTO 90,
Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science 537:409-420 (1991).
Copyright © 1996 by Mark S. Schmalz, All Rights Reserved
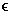 K
and plaintext
a
K
and plaintext
a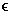 FX.
It is customary that a =
TD(TE(a)).
FX.
It is customary that a =
TD(TE(a)).
